- Offices Time:24 Hours Online
- Email:[email protected]
- WhatsApp:+8618339938759
Posted on September 6, 2022
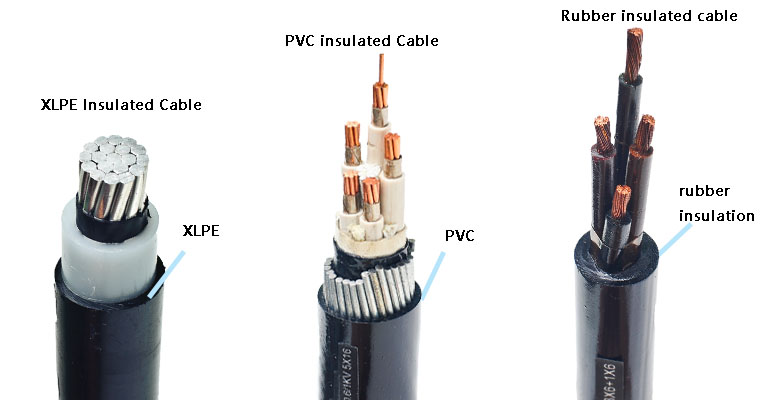
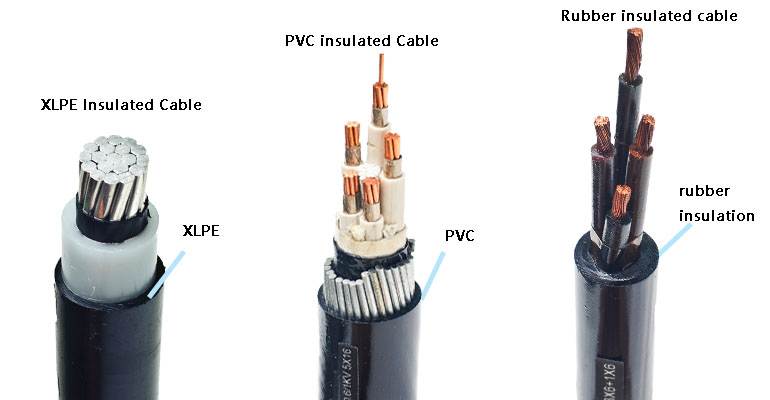
Classification of cable insulation materials
The insulating layer of the cable is used to isolate the multi-core conductors and the conductor and the sheath from each other, and to ensure a certain electrical withstand voltage strength. It should have certain heat resistance and stable insulation quality.
The thickness of the insulating layer is related to the working voltage. In general, the higher the voltage level, the thicker the insulating layer, but not proportionally. Because from the perspective of electric field strength, the thickness of the insulating layer can be thinner when the conductor cross-sectional area of the cable of the same voltage level is large. For cables with lower voltage levels, especially oil-impregnated paper insulated cables with lower voltage levels, in order to ensure that the paper layer has a certain mechanical strength when the cable is bent, the thickness of the insulating layer increases with the increase of the conductor cross-section.
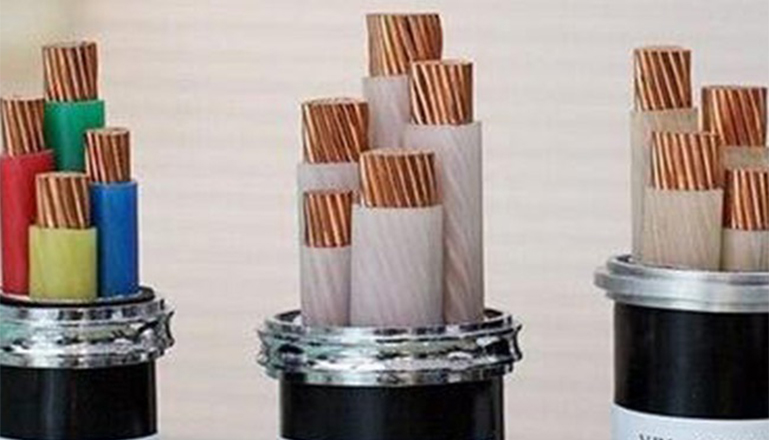
The materials of the insulating layer are mainly plastic and rubber. According to the different materials used for the conductor insulation layer, cables are mainly divided into plastic insulated cables and rubber insulated cables. So let’s take a look at the structure and characteristics of the two insulating materials.
1.PVC Insulation
Plastic insulated cables mainly include PVC insulated cables and cross-linked polyethylene insulated cables. The cable insulation layers are made of thermoplastic plastic extruded and cross-linked after extrusion of thermoplastic polyethylene plastic added with cross-linking agent. This insulation has good electrical properties and water resistance, and can resist acid, alkali, and corrosion. It also has the advantages of high allowable working temperature, good mechanical properties, and the ability to manufacture high-voltage cables.
Polyvinyl chloride insulation has many advantages, but the dielectric loss of its insulation is large, and its conductance (ionic) rises sharply with the increase of electric field strength, so its application at higher voltages is limited. In this respect, the insulation performance of polyethylene is greatly improved than that of polyvinyl chloride. Under the same conditions, the AC breakdown strength of polyethylene is increased by about 60%, and its dielectric loss is only about 0.5% of that of polyvinyl chloride. Polyethylene insulated cable has the characteristics of high insulation performance, small specific gravity, good water resistance and chemical performance, but its melting point is too low, which is prone to cracks under the action of mechanical stress. In order to take advantage of the good insulating properties of polyethylene and overcome the shortcomings of its low melting point, high-energy irradiation or chemical methods are used to cross-link polyethylene, so that its molecules change from the original linear structure to a network structure, that is, from thermoplastic It becomes thermosetting, thereby improving the heat resistance and thermal stability of polyethylene, which is cross-linked polyethylene. Its main features are high softening point, small thermal deformation, high mechanical strength at high temperature, good thermal aging resistance, etc. The maximum operating temperature of the XLPE cable can reach 90 °C. The allowable temperature during short circuit is 250 °C .
Although the XLPE cable has very superior electrical properties, it is inevitable that there will be micropores, impurities and other defects in its insulation, especially the existence of micropores, which enhances its water absorption. The “water branches” phenomenon is induced along the direction of the electric field, so that the insulation is damaged. It is true that the cable’s material selection and manufacturing process to control micropores, impurities, etc. is the main way to reduce the occurrence of water tree branches, but unreasonable construction methods in laying construction will also lead to the formation of new micropores. Due to the poor sealing of cable terminals and intermediate joints, or the water or moisture entering the cable without sealing the broken ends during construction, the cables may cause water tree discharge in the future operation, which should be paid enough attention to.
2.Rubber Insulation
The insulating layer of the rubber insulated power cable is styrene-butadiene rubber or synthetic rubber. The outstanding advantages of this kind of cable are that it is soft and flexible, and is especially suitable for mobile electricity and power supply devices. But the rubber insulation will be damaged quickly when it encounters oil: under the action of high voltage, it is easy to be cracked by corona. Therefore, this kind of cable is generally used for the voltage level of 10kV and below, while the synthetic ethylene-propylene rubber insulated cable can be used for the voltage level of 35kV.
The insulating layer, like the protective layer, shielding layer, sheath layer, and conductor core, is the basic component that constitutes a wire and cable. It ensures that the current or electromagnetic waves and light waves transmitted by the conductor core only propagate along the wire and do not flow to the outside world, while ensuring the safety of external objects and personnel.
Post categories
Most Popular Posts
-
The 135th China Canton Fair
March 20, 2024 -
What are the laying methods of copper core wires and cables?
January 9, 2024 -
What are the advantages of aluminum conductor cables?
December 14, 2023 -
Characteristics of high temperature wires and cables
December 7, 2023





